EV Basics
Learn About the Fundamentals of Electric Vehicles, Chargers and More

Getting to Know the Basics
What Is an Electric Vehicle?
There are three types of electric vehicles (EVs): Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs), Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs), and Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEVs). BEVs are fully electric and must use charging stations to recharge. BEVs are the focus of the EV infrastructure initiative in Kentucky. Often those are the type of vehicle being referred to as “EVs.” The other types of electric vehicles still use internal combustion engines alongside battery power as shown below.
EV Charging Stations
EVs are powered by three types of chargers. Most EV drivers taking local trips charge their vehicles at home, at work or in their communities. Fast charging stations along interstates and parkways help power longer trips.
- Level 1 chargers come with the vehicle and are often referred to as emergency chargers. They plug into a standard wall outlet (120V) but can take several days to fully charge an EV.
- Level 2 chargers use 240V power, which is what is used for large appliances. A Level 2 charger can fully charge an EV in about 10 hours. These are common for home, work, community, park, and retail center charging.
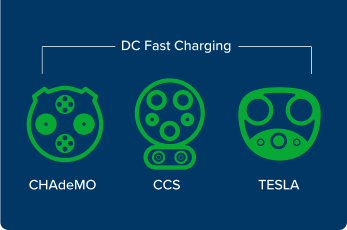
- Level 3 charging refers to Direct Current Fast Charging (DCFC) stations. These are a completely different type of charging because they convert the standard alternating current (AC) power to direct current (DC) power to charge a vehicle much faster. They require much higher power levels and can fully charge a vehicle in 30 minutes. These installations are very expensive and are typically designed to support long distance travel and times when a driver needs a quick charge to stay on the road.
Level 1

+ Standard Outlet
+ Slowest Charging
+ 250 Miles in 48-72 Hours
Level 2

+ “Dryer Outlet”
+ Slow Charging
+ 250 Miles in 10 Hours
Level 3

+ Direct Current Fast Charger (DCFC)
+ Fastest Charging
+ 250 Miles in 30 Minutes
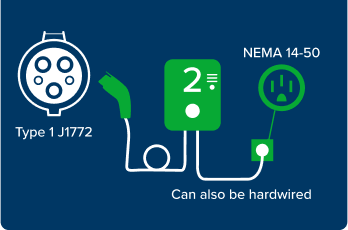
Types of Plugs
The types of plugs for each charging level are shown below. For DCFC stations, the implementation of the North America Charging Standard (NACS) is ongoing and most DC Fast Chargers support the Combined Charging System (CCS). Most EV manufacturers will adopt the NACS plug beginning with 2025 model year vehicles. Adaptors will be available for current owners in the coming months. NEVI requirements for chargers on roads in the Commonwealth will support NACS and CCS charging.
Level 1

Level 2
Level 3
EV Benefits
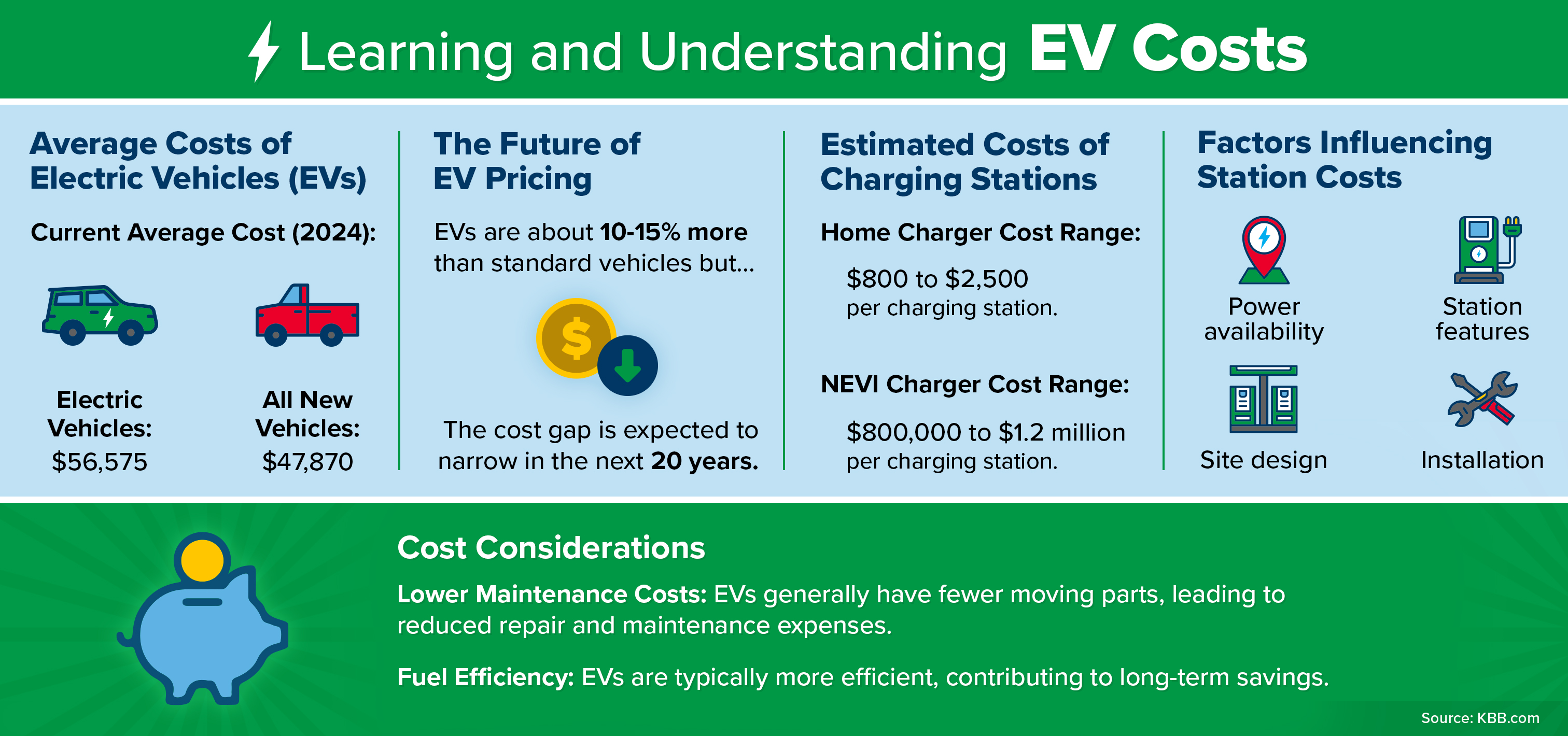
How Much Does an Electric Vehicle Cost?
EV Vocab
Here are some of the common terms and acronyms for electric vehicles.
EV
Electric Vehicle
ICE
Internal Combustion Engine
(powered by gasoline or diesel fuel)
BEV
Battery Electric Vehicle, charged only with a battery
PHEV
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle, uses battery power for the first 20-40 miles and then it uses an ICE
DCFC
Direct Current Fast Charging
EVSE
Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment, typically refers to EV charging equipment and infrastructure
AFC
Alternative Fuel Corridors (Federally defined)
